A complete range of electrical power resistors: GRIDEX® technology

METAL DEPLOYE RESISTOR is the control of resistances for all voltages and all powers, from a few kilowatts to several megawatts.
Thanks to GRIDEX® technology, METAL DEPLOYE RESISTOR provides a technical response adapted to the end use and to high power electrical constraints.
| GRIDEX U | GRIDEX N&F | GRIDEX T |
|---|---|---|

|

|

|
Metal resistors: GRIDEX® technology
The industrial power resistors manufactured by METAL DEPLOYE RESISTOR and marketed under the GRIDEX® brand have remarkable properties:
- Flexibility of use
- Large heat exchange surface
- Robustness
Indeed, they come from an original process creating an electrical circuit by cutting strips in a metal strip: we speak of expanded metal . A variant based on metallic wire woven into an insulating matrix completes the range.
GRIDEX® resistors position METAL DEPLOYE RESISTOR as the leader in electric power resistors. These resistors meet the performance and quality requirements of all sectors of activity with advanced technologies.
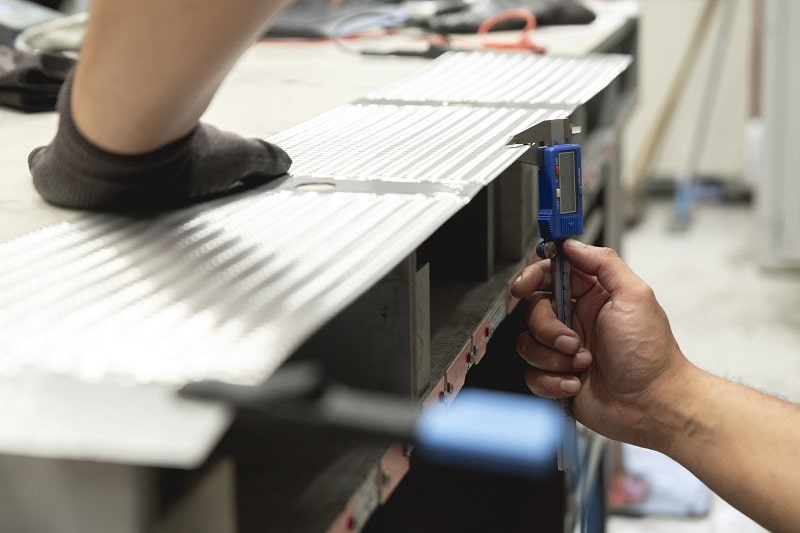
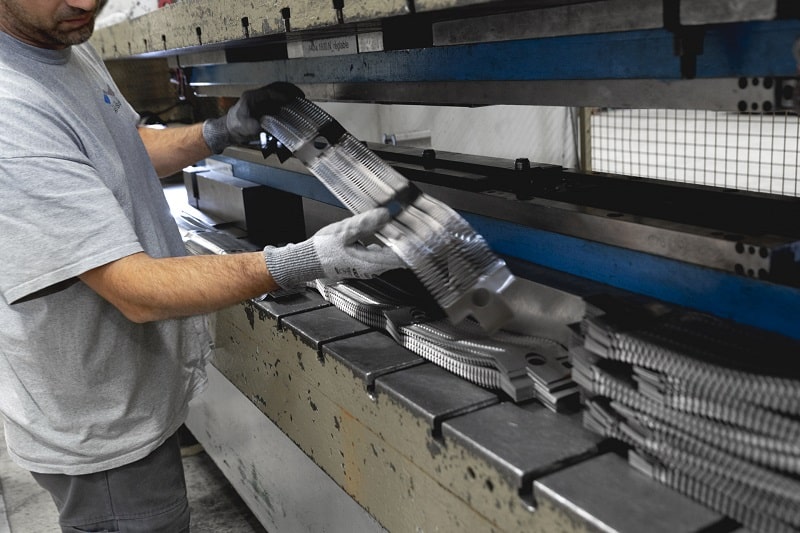


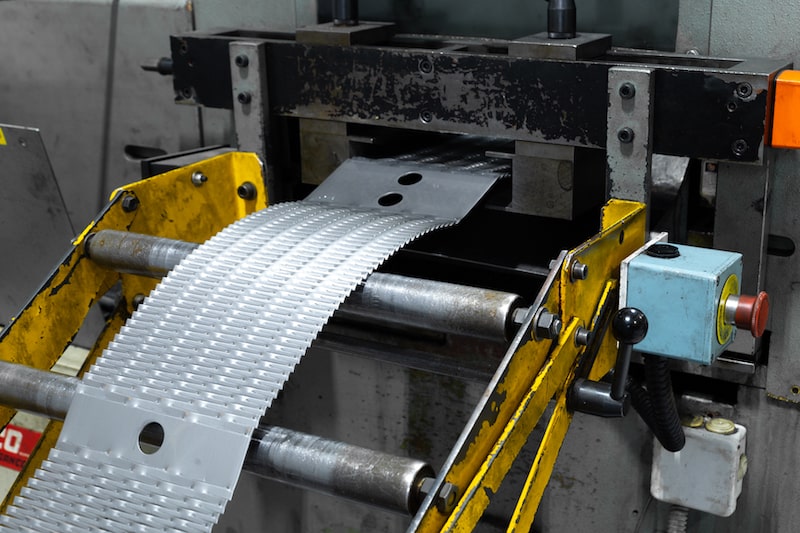
GRIDEX® N & F: Custom grids – Large choice of shapes and sizes

When the time that the electric current passes through a resistor causes heat to dissipate into the ambient environment (non-adiabatic heating), the resistor must offer a structure that promotes heat exchange.
This is the case with GRIDEX® N & F.
GRIDEX® N = natural convection and adiabatic operation
GRIDEX® F = forced ventilation
GRIDEX® N & F use expanded metal grids as resistive elements
These grids have a deployed part (the resistive part) and 2 solid bands (one at each end) to ensure assembly and connection. A shape can be given to the elements to improve their mechanical resistance. The choice of the type of element is based on the resistance value, the energy to be dissipated and the mechanical rigidity.
Assembly of resistive elements
The resistive elements are stacked on threaded rods and welded together for an optimal electrical connection.
Insulation
Insulation between the resistance elements themselves and the rods is ensured
- or by ceramics for standard uses
- or by mica tubes and washers when the resistance is subjected to strong vibrations (railway traction resistance).
Heat dissipation
The resistant elements of expanded metal offer an optimal surface of dissipation either by natural convection or by forced convection.
Resistance precision
The geometry of the resistant elements in expanded metal and the variety of meshes allow us to obtain resistive elements with a high precision of ohmic value.
Flexibility
The use of expanded metal elements allows in most cases to adapt to tight spaces and optimize the weight.
Uses
- Dynamic braking (forced ventilation or natural convection)
- High voltage grounding
- High power harmonics filtering
- Load banks
- Drying
Alloys
The different types of alloy used are:
- Ferritic steel
- AISI 304
- 18/10 stainless steel
- Refractory steel
- Cupro-Nickel Alloy
- Aluchrome
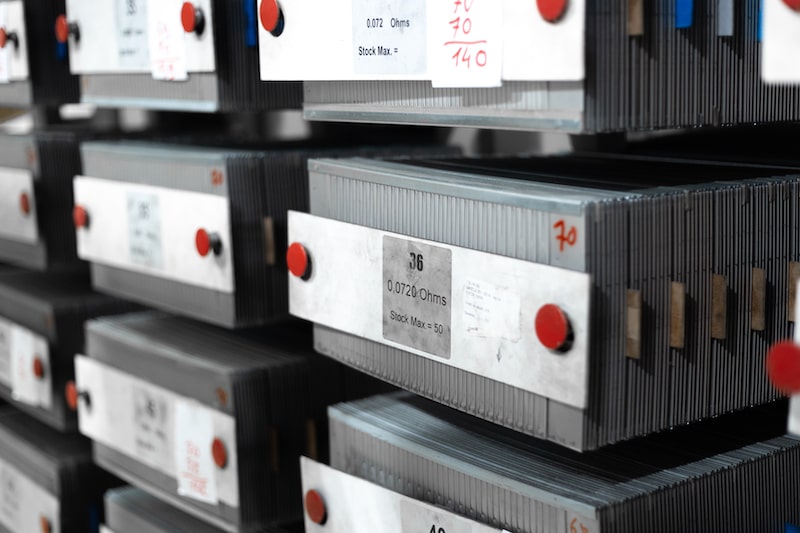
GRIDEX® U: Standard grids – 52 references for 52 resistive values

When it comes to routine application, whether the time is short or long, GRIDEX® U, although more sober in design, offers similar technical capabilities to GRIDEX® N&F.
GRIDEX® U is formed by a very elongated diamond mesh and lateral stiffeners.
Its strengths are numerous:
- Excellent thermal dissipation
- Mechanical fixing of resistant elements by full bands, of temperature lower than that of the active part
- Increased service life of the resistant elements themselves and of the retaining and insulation
- Great robustness mechanical montages
- Almost automated manufacturing, thanks to its geometry
DESCRIPTION
The Gridex® U system is made up of collections of edged grids :
- on the two short sides by full adhesive bands intended for the mechanical fixing and arrivals of current
- on the two long sides by profile stainless steel stiffeners in U. Insulating tape ( mica sheet ) flexible which fits inside the stiffener while extending far beyond the insulation between the latter and the edge of the wire rack .
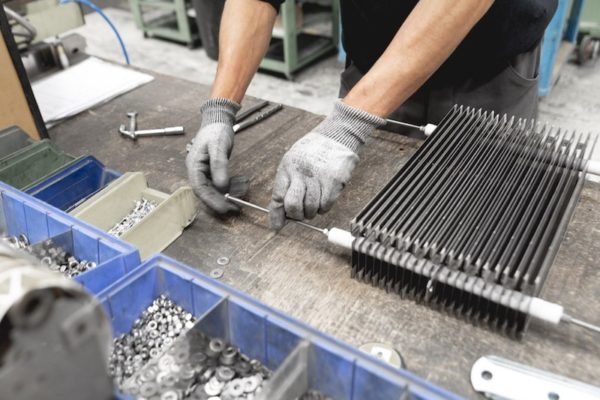

ASSEMBLY
The grids are stacked on two rods, threaded at the extremities. Isolation between the grids and the rods is ensured by ceramicflange rings . The assembly is locked by nuts and spring washers.
LOGIN
The connections between grids are ensured by spot-welded stainless steel jumper connections .
These jumpers give good mechanical rigidity to the whole bank. They are doubled in case of strong currents .
RANGE
The configuration of RU grids allows to obtain from the standard dimensions (180 x 360) ohmic values varying from 0.0114 to 12.7 ohms per grid depending on the thickness (from 0.4 to 2 mm), the alloy used or the mesh.
The grid can withstand a voltage of 600V or 1.2 kV in lightning impulse according to the chosen manufacturing technique.
USES
- High voltage grounding
- Harmonics filtering
- Load bank
- Motor control
ALLOYS
The different types of alloy used are:
- AISI 304
- 18/10 stainless steel
- Refractory steel
- Cupro-Nickel Alloy
- Aluchrome
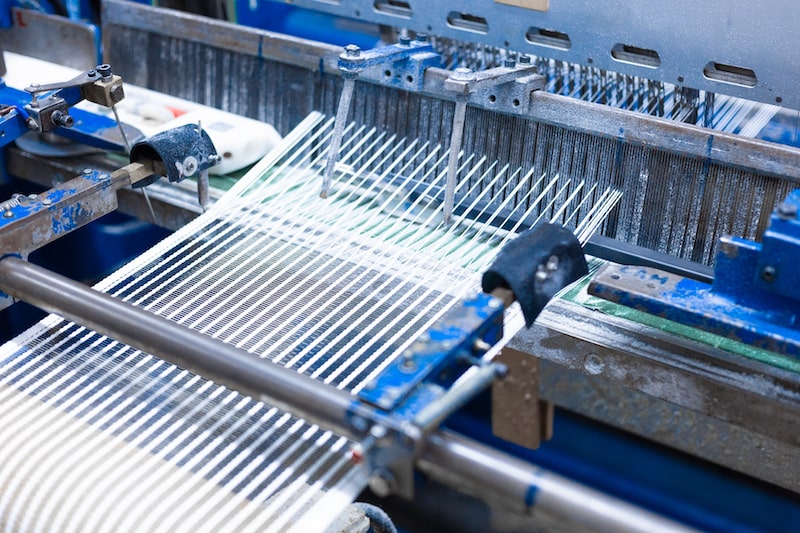
GRIDEX® T: Woven resistors – High resistive values and high voltage
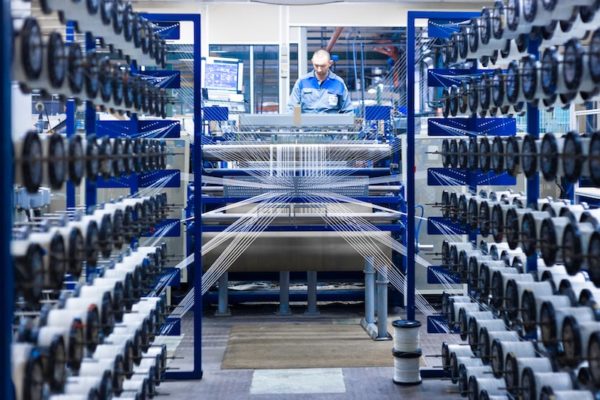

GRIDEX® T resistors are made of woven elements. The warp wire is electrical insulator, the weft wire is resistive. This technique makes it possible to achieve high ohmic values (several hundreds to thousands of ohms) and is particularly suitable for applications requiring high voltages (continuous or transient).
THE RESISTIVE WIRE
Most of the time, an alloy of nickel and chromium, the wire has a diameter of a few tenths of a mm. Other shades can be used to obtain particular properties.
THE CHAIN WIRE
It is used to hold the resistive wire firmly in place without altering its heat exchange coefficient. It is made of silica fiber.
This material has many advantages
- Resistance at high temperatures: up to 600 ° C
- Coefficient of expansion low linear thermal: the length of the fabrics varies very little under the action of temperature, which facilitates fixing
- Excellent hold hot mechanical tensile stress
- Good resistance to pollution
DIMENSIONS AND ASSEMBLY OF ELEMENTS
The canvases are of variable length and width to suit all needs.
End bands are used for fixing and tensioning the canvas
In most cases, the fabrics are arranged in rows and connected in series or in parallel or both at the same time.
USES
- Harmonics filtering strong power .
- Capacitordumping at high tension .
- Infraredheating.
- Applications requiring a specific mechanical design (case of small units heatingunits ).
ALLOYS
Different alloys are available as standard:
- stainless steel
- iron-chrome-aluminum alloys
- etc …
When does your experience with METAL DEPLOYE RESISTOR begin?





















